Already well-known in the industry for their rock-solid reliability and resiliency, Haivision’s Makito X4 Video Encoder and SRT Gateway video stream router, include Path Redundancy, a hitless failover feature that ensures uninterrupted low latency real-time video transport. In this post, we’ll explain how exactly this important new feature works, as well as the benefits it offers to users.
What is Path Redundancy?
Path Redundancy is an important feature from Haivision included with the Makito X4 and Maktio X4 Rugged video encoders as well as the SRT Gateway stream routing solution. Path Redundancy is a type of hitless protection and failover technology that relies on more than one IP network path to prevent disruption to live video streams, in the event of network congestion or outages, by maintaining continuity of service.
Path Redundancy increases the reliability of live contribution, content distribution, and edge to cloud workflows, allowing them to leverage multiple network paths to ensure that live streams are successfully transported from one location to another. Path Redundancy enables continual routing of live video streams even if one IP network path fails or experiences temporary issues such as packet delivery delays and sudden bandwidth constraints, ensuring high-quality feeds for must-not-fail event coverage or mission-critical ISR applications.
Similar to SMPTE-2022-7 over managed networks, Path Redundancy adds seamless stream protection and hitless failover to Haivision solutions. When combined with the already reliable nature of the Secure Reliable Transport (SRT) protocol, Path Redundancy makes live video transport over the internet an extremely reliable and cost-effective option compared to using satellite links or dedicated fiber.
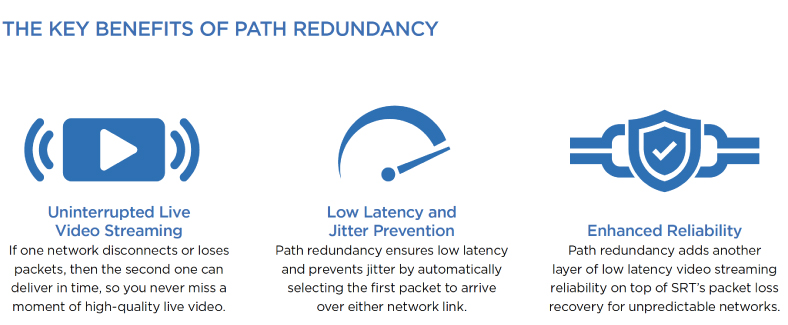
What are the Benefits of Path Redundancy?
Whether for live coverage of premium sports and news events, real-time ISR video streams, or global video production collaboration, Haivision Path Redundancy provides a high level of reliability and peace of mind to broadcast engineers and network operators.
As Corey Behnke, co-founder and producer at Live X, a full-service production company in New York, explains “For those just-in-case moments when you never know what’s going to happen, Path Redundancy is an incredibly valuable and must-have feature for broadcasters to insure against potential failures.”
How Does Path Redundancy Work?
Path Redundancy can route live SRT streams over two or more network paths in real-time. Each network path can use its own combination of IP address and port number or IP socket. Ideally, each network path should be sent over separate NICs (network interface cards). Haivision SRT Gateway appliances include 2 ethernet NICs, while the Makito X4 video encoder supports a second NIC via an SFP adaptor. Using separate NICs enables an SRT stream to be routed over completely separate IP networks, typically two different ISPs or two different data links.
Haivision Path Redundancy supports two modes: Active-Active and Active-Backup.
Active-Active Mode
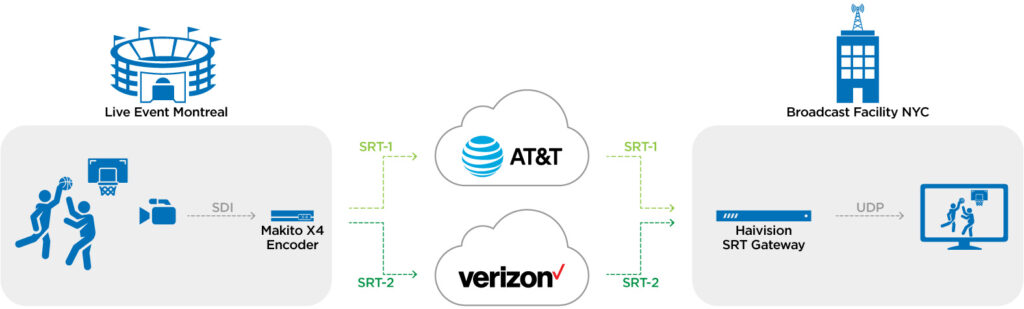
In Active-Active mode, Haivision Path Redundancy provides a high level of live stream reliability required for broadcasting live events such as news and sports. Two identical SRT streams are simultaneously sent over two or more network links. Though the streams take different routes, they are sent to the same receiver or SRT listener which accepts the first packet to arrive, over whichever network.
The broadcast use case illustrated below shows how path redundancy can be applied to remote production with a Makito X4 video encoder sending two SRT streams to an SRT Gateway using two different network providers. As the receiver, the SRT Gateway accepts the first packet to arrive from either network, enabling very robust, hitless redundancy, with no glitches.
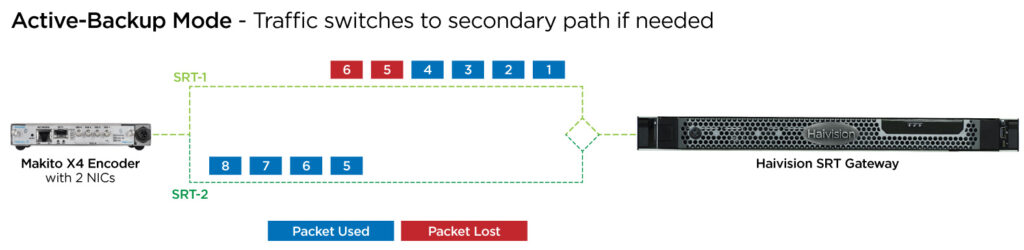
Active-Backup Mode
Active-Backup mode offers bandwidth savings by, for example, using a broadband internet provider as a primary network path and a different, secondary provider, such as a 5G mobile network, as a backup.
If the primary or active path fails, there is an automatic immediate switch over to the backup network. The backup path has an SRT connection open, but because there’s no actual transport happening, it is essentially idle. As in the use case below, when the Haivision SRT Gateway receiver detects a loss of connection it will then switch automatically from the active primary stream to the backup stream to ensure uninterrupted streaming of live content.